JUVENILE, ADENOMATOUS POLYP
- Feb 9, 2020
- 1 min read
Updated: Jun 16, 2020
Juvenile polyp

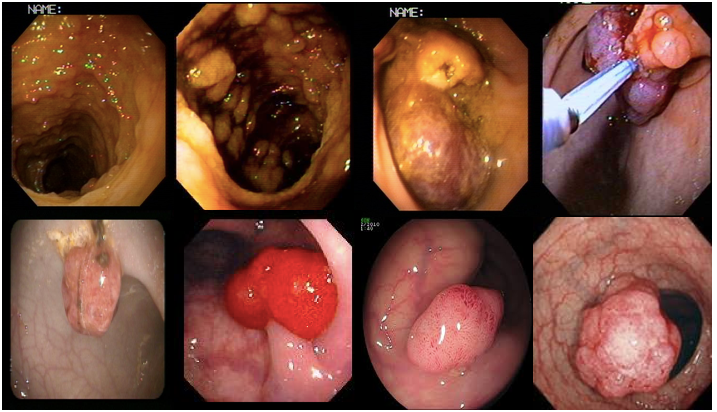
Lesion: Two-year-old boy presenting with a ‘prolapsing mass’. Colonoscopy revealed an isolated juvenile polyp which was removed by snare polypectomy. Histology confirmed a juvenile polyp.

- Pedunculated juvenile polyp
- Treatment: polypectomy
- Large juvenile polyp in the descending colon
- Treatment: polypectomy.

Management
ESGE/ESPGHAN suggest removal of very small polyps (< 3mm) by cold biopsy forceps and 3–8mm polyps by hot or cold snaring. Cold snaring is advisable in the right colon where the perforation risk is higher. For polyps > 8 mm, hot snaring is suggested
Adenomatous polyps

Multiple adenomatous polyps identified at sigmoidoscopy in a 15-year-old boy being screened for familial adenomatous polyposis due to a maternal familial adenomatous polyposis history.
Treatment: polypectomy, surveillance every three years.
FAP

Multiple colon polyps in a 5 -year-old-boy with FAP
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene.
Intestinal polyps: Endoscopic findings




Comments